Cloud Computing
- Delivery of computing services over the internet.
- Enables faster innovation, flexible resources and economies of scale.
Public Cloud
- Owned by cloud services
- Provides resources and services to multiple organizations and users.
- Accessed via secure network connection.
Private Cloud
- Organizations create a cloud environment in their data center.
- Organization is responsible for operating the services they provide.
- Does not provide access to users outside of the organization.
Hybrid Cloud
- Combines Public and Private clouds to allow applications to run in the most appropriate location.
| Public Cloud | Private Cloud | Hybrid Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| No CapEx to scale | Hardware must be purchased for start-up and maintainance | Provides most flexibility |
| Application can be Applications can be quickly provisioned and deprovisioned | Organizations have complete control over resources and security | Organizations determine where to run their applications. |
| Organizations pay only for what they use | Organizations are responsible for hardware maintenance and updates | Organizations control security, compliance, or legal requirements |
Cloud Benefits
- High Availability
- Scalability
- Global reach
- Agility
- Disaster recovery
- Fault tolerance
- Elasticity
- Customer latency capabilities
- Predictive cost considerations
- Security
CapEx vs OpEx
| CapEx | OpEx |
|---|---|
| up-front spending money of physical infrastructure | Spend on products and services as needed |
| Costs have a value that reduces over time | Get billed immediately |
Consumption-based model
- Only pay for the resources used
Benefits
- Better cost prediction
- Prices for individual resources and services are provided
- Billing is based on actual usage
Cloud Services
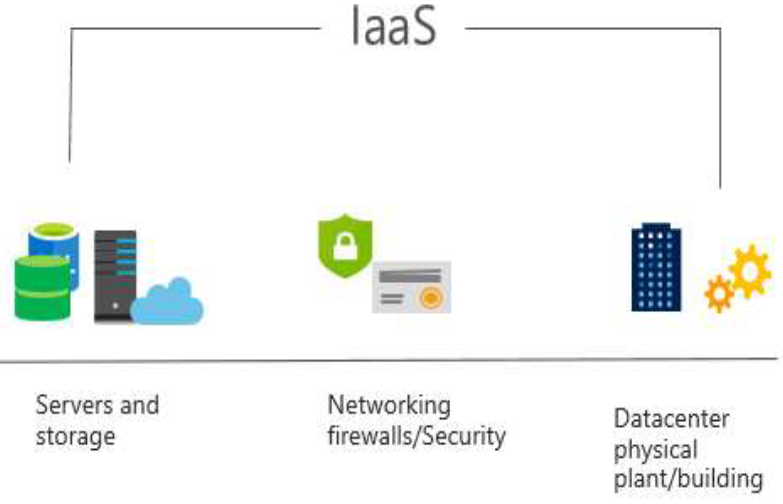
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Renting servers, virtual machines, storage, networks, and operating systems from a cloud provider
- Video Explaination
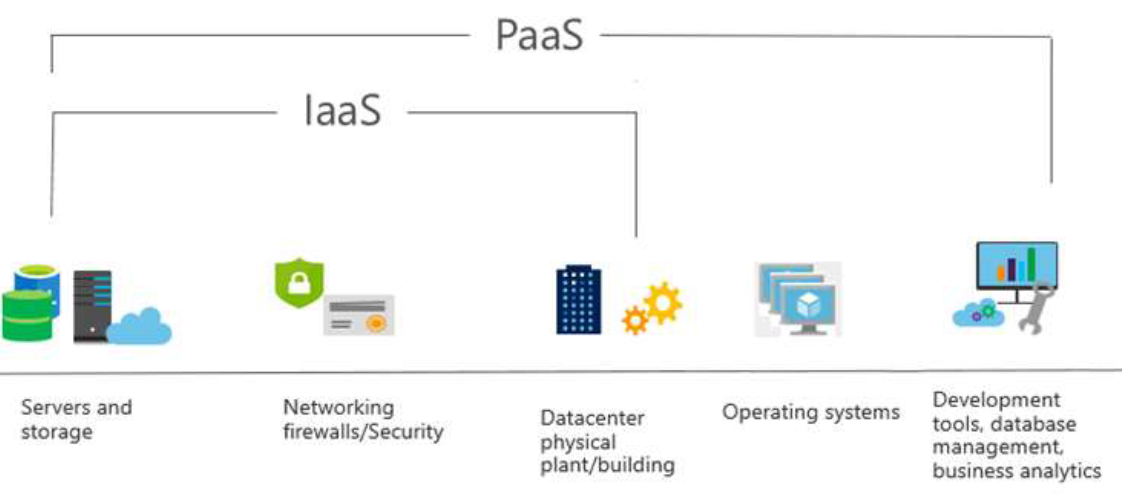
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Provides environment for building, testing, and deploying software applications
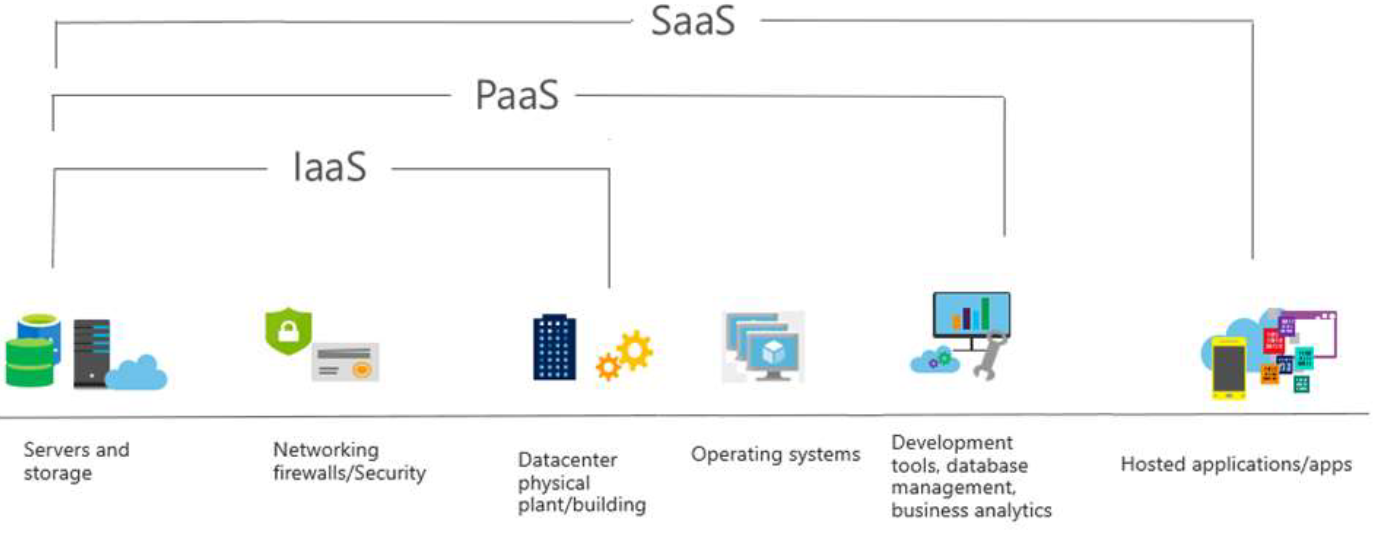
Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Using cloud-based apps over the internet.
| IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
|---|---|---|
| Most flexible cloud service | Focus on app development | pay-as-you-go |
| Configure and manage the hardware for your application | Platform management handled by the cloud provider | Use the software on a subscription model |
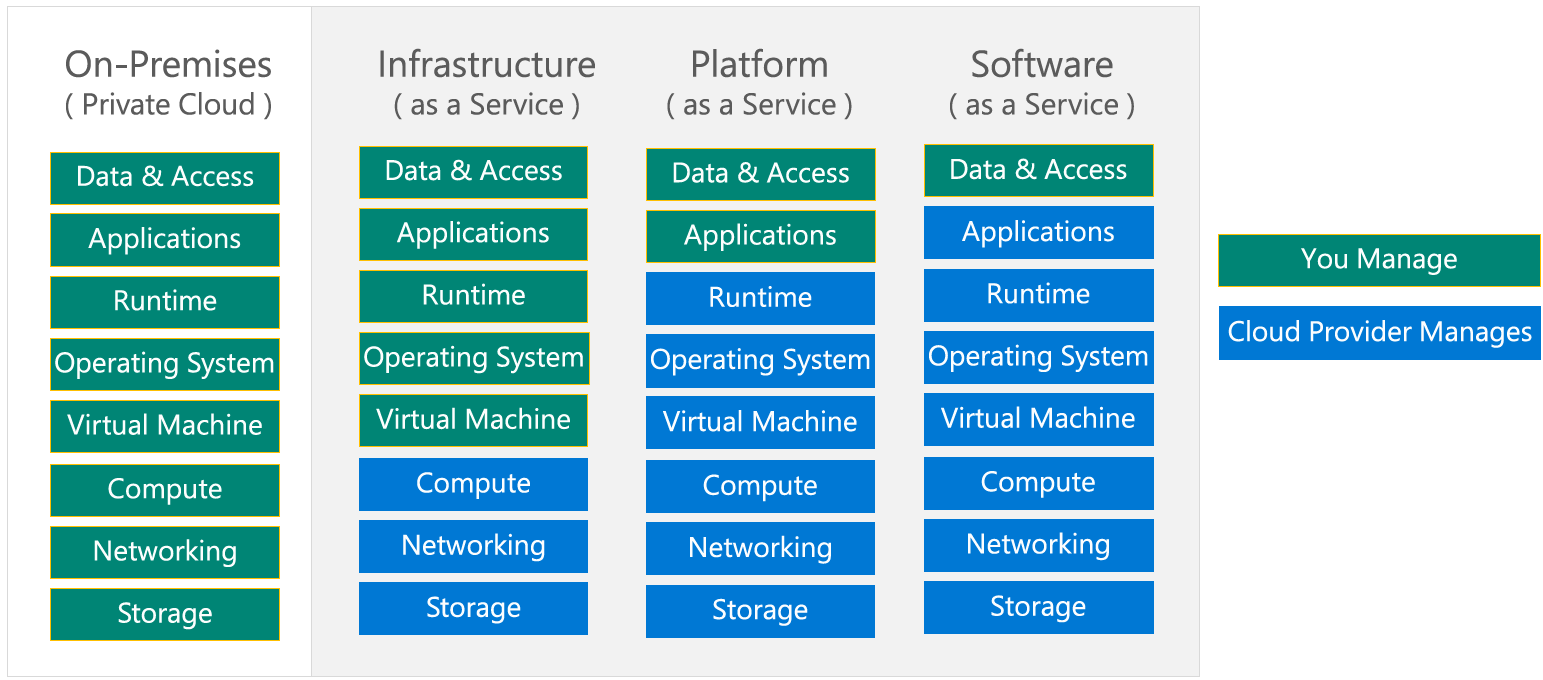
Shared Responsibility Model
Serverless Computing
The cloud service provider automatically provisions, scales, and manages the infrastructure required to run the code.
Azure Functions
Azure Functions is code running your service and not the underlying platform or infrastructure. It creates infrastructure based on an event
Azure Logic Apps
Azure Logic Apps is a cloud service that helps you automate and orchestrate tasks, business processes, and workflows when you need to integrate apps, data, systems, and services.